In part 1 of this series, Your Pain Relief Plan Introduction I discussed why we feel pain and introduced the concepts that the degree of pain felt could vary widely from one individual to the next due to lifestyle factors. Also, when long term, typically over 3 months, the brain would lock the pain in. Emotional trauma, even as far back as childhood, has been found to lock in pain for almost a lifetime.
In part 2 of this pain relief series, I will get into more detail about how pain works and discuss the implications of aging and the differences between acute and chronic conditions and the most effective ways of treating these. But first, a quick look at the brain, how it has evolved and how this relates to processing pain.
Read on
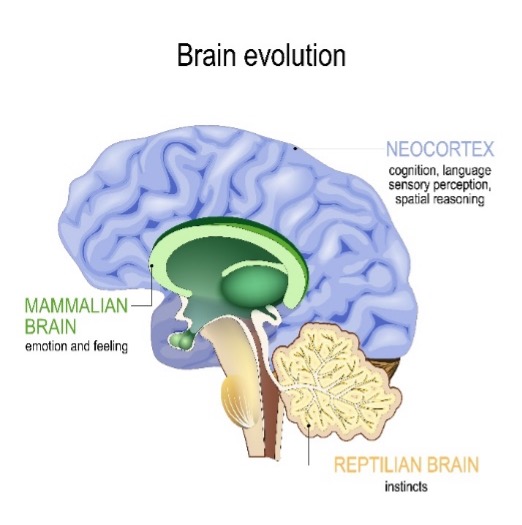
The oldest part of the brain is the reptilian brain, which deals with basic survival instincts. Next came the mammalian brain, which added the ability to feel emotion. The third part is the human brain, the Cortex, which gives us our human qualities of cognition, sensory perception and spatial reasoning and is in charge of the human decision making process.
Your nerves transmit pain signals. Inside your nerves you have sensors for temperature, stress, movement, pressure, immunity molecules and blood flow. Similar to car sensors, any damage or fault to any of these sensors will put a light on your dashboard, to alert you of a problem. The nerve does the same thing by increasing pain.
These pain impulses travel up the spinal cord, to a part of the brain which acts like a router (called the thalamus, which sits on top of the reptilian brain) and as a simple analogy, this router makes phone calls to other parts of the brain. Thus it acts like a hub on a wheel, sending out and gathering information from various parts of the brain. For example to:
- the sensory cortex (which interprets the sensory nature of the pain)
- the mammalian amygdala (which assesses the level of fear, as it is the emotional centre, and decides if the body needs to shut down digestion, cell division, circulation etc.)
- the neocortex (which is in charge of the human decision-making process).
Once information is gathered, the thalamus sends it forward, like a train leaving a station, through the limbic system ( the mammalian brain) where emotions are added on the train journey. Thus a person who is fearful or anxious will feel more pain. The train journey ends at the human brain where a decision of the level of pain felt is made. It is vital to understand that the degree of pain felt is not directly related to the initial cause of the pain signal, as there are many factors to consider, such as:
- Body sensation and location
- Movement – muscles may need to brace the area
- Focus & concentration
- Fear response
- Memory area recalling previous similar experience
- Motivation - processes pain
- Stress response - weight, digestion, sleep, temperature
All factors interact to decide on the suffering experienced. This may have little to do with the degree of injury and hence makes it clear that a qualified and knowledgeable therapist is needed to properly diagnose and treat the injury.
The Consequences Of Aging
As we age, we need to put more care into diet, supplementation, exercise, and our workload. It sounds simple, but many of us fail to even acknowledge that as we get older, we have to change the way we use our bodies. As we age, naturally occurring enzymes are fewer, inflammation is greater, and the production of inflexible scar tissue becomes much more extensive. Therefore, long-term solutions for pain relief also need to address our ongoing biochemical changes.
Sleep quality tends to deteriorate and ongoing deprivation can lead to symptoms virtually indistinguishable from widespread pain, fatigue and diffuse tenderness. Early evidence also shows that anxiety, depression and sleep disturbances have been common reactions to the COVID pandemic. Thus the problems faced by Long COVID sufferers are likely to be with us for many years to come.
What is the difference between Acute and Chronic Pain?
Acute pain is a safety mechanism located in the reptilian brain, the oldest part of the brain. It’s this ancient reflex system that makes you quickly take your hand out of the fire. Acute pain is typically pain which has resulted from a recent injury, such as a twisted ankle, bruised or torn muscle. In most cases acute pain needs immediate treatment and is usually resolved within a few treatment sessions combined with exercise prescription.
Chronic pain, by its nature, may not be resolvable
Chronic pain is long term pain, beyond 3 months, as the brain has hard wired the pain in by that time. Chronic pain can occur because of numerous conditions, such as emotional pain, joint wear and tear (osteoarthritis), spinal disc thinning, bulging or rupture, bone thinning (osteoporosis), unresolved tendon or ligament damage, to name but a few. Chronic pain, by its nature, may not be resolvable. It may need a lot more treatment than acute pain to bring down to acceptable levels and will benefit greatly from ongoing maintenance or wellness treatment to prevent reoccurrence.
Modern science confirms benefits of a more holistic approach
Latest neuro imaging technology, which can see the electrical activity in the brain in response to different lifestyles, has allowed the world to delve deeper into the understanding of chronic pain. It has confirmed that pain is modulated by factors such as attention, anticipation, empathy, placebo, meditation, fear, anxiety, posture, emotion and movement. This, in turn, has confirmed the benefits of a more holistic approach to assessment and treatment.
This new insight into chronic pain helps explain why, for example, X-rays showing the degree of osteoarthritis in joints has no correlation to the pain being felt.
To summarise, we have shown how each persons brain can process pain differently, to the extent that one person may feel tremendous pain, when another, with essentially the same condition, might feel little or no pain at all.
The availability of latest MRI scanning technology has verified that many non physical factors can impact the way pain is handled in the brain. This in turn supports the benefits of a more holistic approach to assessment and treatment.
Acute problems are usually caused by a recent injury and are best treated promptly, whereas chronic problems are longer term and tend to be related to the aging process. Chronic pain in many cases cannot be resolved and lends itself to a longer term control of symptoms, rather than treatment of root cause as with an acute injury.
In my next blog Your Pain Relief Plan Part 3 I will explain neuropathic pain and the effectiveness of both exercise and drugs and where these may be the wrong solution.
If you are in pain, then it’s important to get help as soon as possible. It is even more important if you have been in pain for an extended period, as you may be risk of your pain becoming locked in and the degree of pain you may feel may not be consistent with the severity of the cause.
Call 01889 881488 Now
p.s. Don’t try to book online at this time as that is only suitable for existing clients already being treated for an existing problem.
In my two previous blogs A Different Perspective On Your Physiotherapy Assessment and The Subjective Physiotherapy Assessment, I discussed the importance of getting that connection and really listening to get the patients story. Why are you here, what are your beliefs about treatment?
Now it’s time to go further, honing it down with specific questions about the problem.
Let’s use an example to help illustrate. Someone comes to me and they've had chronic pain in their foot for a very long time. I would be asking questions about the possibility of arthritis. Questions regarding the nervous system. Looking at the way that the body moves. Seeing if the pain is transmitting down from the spinal cord, because it could be a problem in the spine itself and not the foot at all. Having a look at the function of the foot, seeing if biomechanically the patient is walking in a strange way, and is that is making it worse?
How does it feel? How does the tissue feel? Is there any swelling? Are there problems with circulation? Is the sensation there? Are the nerves working properly? Is there an amplification of pain so that when I touch, the tissue is overly sensitive? What are the clues as to what's going on?
This is a very important start to this part of the assessment, which leads to the physical assessment.
To recap, the first part is establishing the connection and the story, the background, the beliefs, the values. The next part is to do with the Four Keys, to do with your immune system and your general health.
The next part is to hone it down into the particular problem today and how it's starting to manifest itself physically.
The final step is to go into the physical, which we can't do remotely by zoom. The physiotherapist has to get hands-on and assess physically, face to face.
In my next blog The Physical Assessment I will delve into the actual hands-on physical assessment. Many of you may have thought that this would be the first step in an assessment and that is the mistake that so many make, missing out on the vital steps of building connection and trust and gaining a deeper understanding of the all-important beliefs of the client. Make that mistake and you are destined to gain so much less.
In the meantime, if you are in pain right now and you feel confident we can help, then why not call now. Erica, Jean and Charlotte will be happy to help
Call 01889 881488 Now
p.s. Don’t try to book online at this time as that is only suitable for existing clients already being treated for an existing problem.
I get asked a lot of questions about physiotherapy assessment. What do we do at my clinic? How do I assess? How do I teach assessing?
In my previous blog A Different Perspective On Your Physiotherapy Assessment, I mentioned that the first and most important thing is to have a safe, quiet environment that builds a connection and trust. If you don't feel that with your physiotherapist, you're not going to want to proceed to any kind of medicine or treatment and your outcome won't be as successful. There won't be that connection.
To recap, the most important thing for the patient is that the physiotherapist has created a sacred space, a quiet office, where the phones are switched off, the computer is not a distraction, and you eyeball each other to get that connection. And then your physiotherapist listens to your story. And how you describe what's going on with you. And then, in that moment of connection, your physiotherapist can get glimpses of the real authentic self behind the story, who you really are.
Once your physiotherapist glimpses the story of the problem, he or she can start to elicit some background which is past medical history. So we'll ask questions like the health of your family to see if there are relevant genetic links. We may also explore your beliefs and values and more about your family so we'll know how difficult it is for you to attend and for you to have the necessary treatment. We may touch on your past experiences of treatment because if you've been scared or let down previously, you're going to have very different expectations. We need to address that head-on.
And then, of course, my favourite four keys questions (see my first book ‘The Four Keys To Health’ available on Amazon), which looks into your mindset, lifestyle, fitness and what you eat. All these help us assess how well your immune system is working, and your general health, which helps refine our treatment prescription.
That, in a nutshell, is the first part of the physiotherapy assessment.
In my next blog ‘The Subjective Physiotherapy Assessment – Part 2’ I will continue on this journey of helping you understand how to really get the most out of this process.
In the meantime, if you are in pain right now and you feel confident we can help, then why not call now. Erica, Jean and Charlotte will be happy to help.
Call 01889 881488 Now
p.s. Don’t try to book online at this time as that is only suitable for existing clients already being treated for an existing problem.
